What is a smart home? How does lighting work in it? What does this give the consumer? Consider these issues in this article.
The definition of a smart home
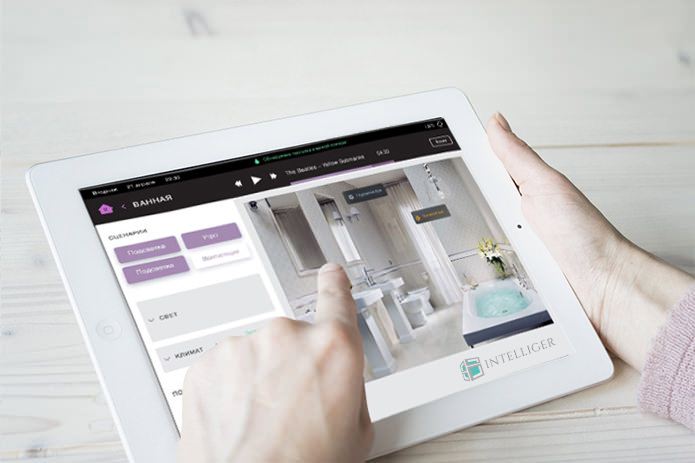
An integrated control system for all the engineering equipment of a building is called a “smart home”. Such a system is built on a modular principle, which makes it easy to change and expand it without losing any existing functionality. Modules - control lighting, climate, security systems and so on.
No matter how perfect the individual engineering subsystems are, only centralized management makes them all a “smart home”. It is based on specific wiring and a set of automation equipment. As a result of integration, each part of a single whole works in close interconnection with other elements. Consider this as an example of lighting.
Smart home lighting control
The way in which the lighting of a “smart” house is controlled is technically more complicated than the “classic” one, but it is easier for the user. All the complex logic of work is laid at the design stage, and control is displayed on a convenient panel with a single interface. Moreover, it is not only about turning on and off the lighting devices. Important elements involved in imparting lighting control to intellectual properties are:
- Motion / presence sensors, contact sensors that turn on or turn off the light at home at a certain moment. For example, JUNG mini-sensors based on the KNX standard, GIRA weather station with a set of sensors.
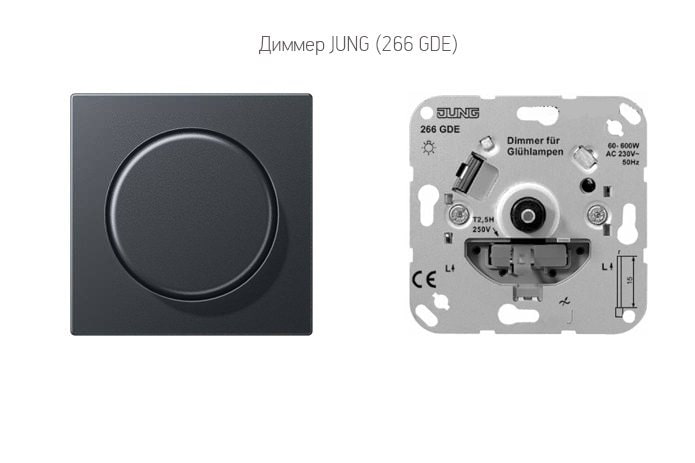
- Dimmers that smoothly change the brightness.
- Motorized curtains, blinds, roller shutters, electric cornices, through which the balance between natural and artificial light will be regulated.
- Lighting devices, which can be either ordinary or smart on their own. Moreover, they can be used separately or as an element of a single system. For example, Philips Hue bulbs or the “smart” VOCCA cartridge.
- System equipment, including control panels and logic modules, connected together by special wiring.
Not only in interaction with each other, but also with other engineering subsystems, this equipment, as part of the “smart home”, allows you to achieve amazing comfort along with the economical use of electricity. Let us dwell on this in more detail.
What gives the user “smart” lighting control?
The end consumer is uninterested in the technical details of a particular equipment. More noteworthy are the features that are available through its use. With the help of "smart" lighting control are possible:
- Notifications. What to do when the house has loud music and a doorbell sounds? In the era of home automation, this does not go unnoticed. The system is configured so that if music is turned on, the lighting will blink a couple of times when you press the doorbell bell. Here the role of integration is manifested when one engineering system (light control) works in conjunction with others (security system and multimedia control).
Other events can be handled. The motion sensor will turn on the backlight of the corridor when the child wakes up, will not let him stumble when it is dark.When the sensor is triggered, the system can be programmed to turn on dim light at the same time in the parents' bedroom to signal a situation. Convenient and safe. Automatically without human intervention, the algorithms laid down at the design stage are executed.
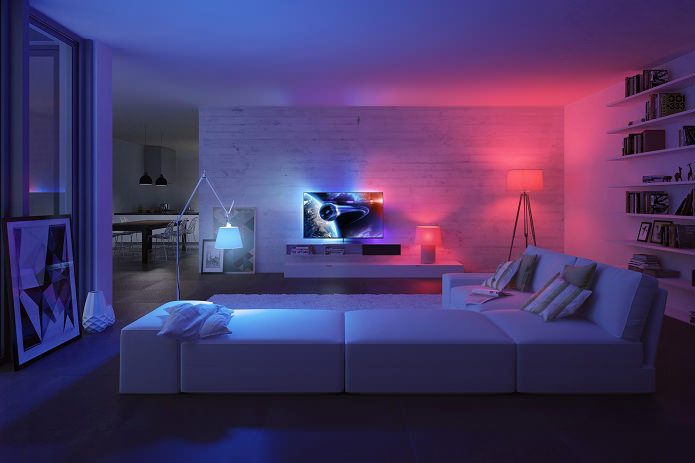
There are light bulbs that change color (Philips Hue). Using the special Taghue application, they can be configured to trigger messages from social networks and email clients. Now, just being next to such a lamp, you can instantly find out about the arrival of a new message by its color. And then take the necessary actions.
- The work of sensors. Thanks to the sensors, it is possible to unleash the potential that smart control of lighting has. Here, security functions intersect with lighting. The illumination of the track at the house, which is turned on by the motion sensor, will not only create comfort when moving at night, but will also serve as a means to deter intruders.
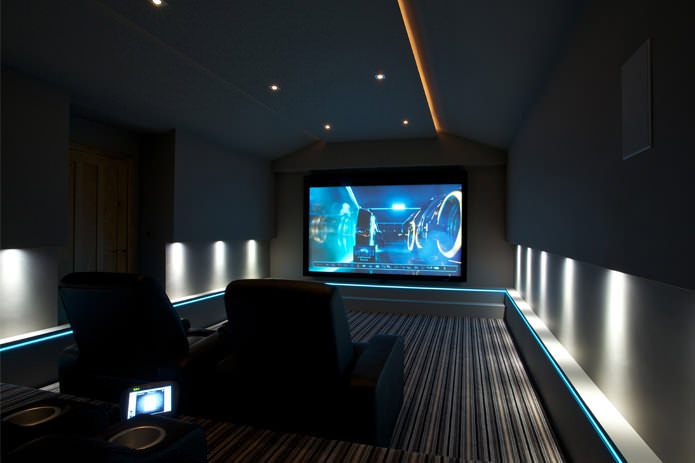
When the home cinema is located in the basement, the script starts on the door contact sensor: while the door is open, the light turns on; with the door closed, if there are people in the room (the presence sensor is working) and the equipment is turned on, after a while the light is dimmed to watch a movie, and the corridor lighting in front of the cinema is turned off. After viewing, everything happens in reverse order.
- Flexibility in creating the necessary atmosphere and decor. The desire for new sensations always comes more often than possible to make a radical change or repair in the house. With an instant change in the parameters of the fixtures (color, brightness, directivity), as well as the ability to create new scenarios (a series of actions performed by an event or when a button is pressed), the atmosphere in the room changes beyond recognition.
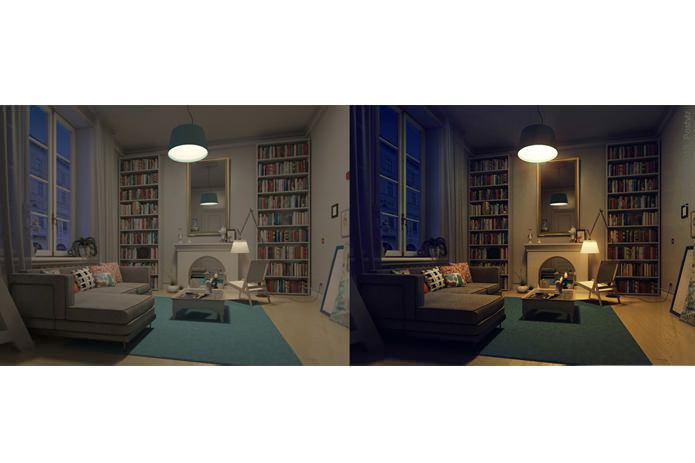
- The balance between natural and artificial lighting. Do not turn on the lights in the morning if you can smoothly raise the curtains, letting in the sun. This is how the “morning” scenario works, working every day. If the weather is bad, the weather station sensors or a separate light sensor will inform the system about the lack of sunlight, and that it is necessary to increase the brightness of the lamps.
So, lighting control includes all of these features, but is not limited to them. Using modern professional smart home systems, there are no restrictions on the imagination and the needs of the owner. As a cheaper option with minimal, but sufficient functionality, separate devices, such as the Philips Hue bulbs or the “smart” VOCCA cartridges, are used. All this provides maximum comfort and a high degree of efficient use of energy resources - something without which it is already difficult to imagine a modern house.











 Top 10 Trends in Interior Design 2020
Top 10 Trends in Interior Design 2020 Rating of cheap TVs with Smart-TV
Rating of cheap TVs with Smart-TV New Year's LED garlands on AliExpress - we disassemble while it's hot, so that the house is bright
New Year's LED garlands on AliExpress - we disassemble while it's hot, so that the house is bright Wall mural with flowers in the interior: living wall decor in your apartment
Wall mural with flowers in the interior: living wall decor in your apartment Gray sofa in the interior: views, photos, design, combination with wallpaper, curtains, decor
Gray sofa in the interior: views, photos, design, combination with wallpaper, curtains, decor Interior in peach tones: meaning, combination, choice of finishes, furniture, curtains and decor
Interior in peach tones: meaning, combination, choice of finishes, furniture, curtains and decor